Locally made
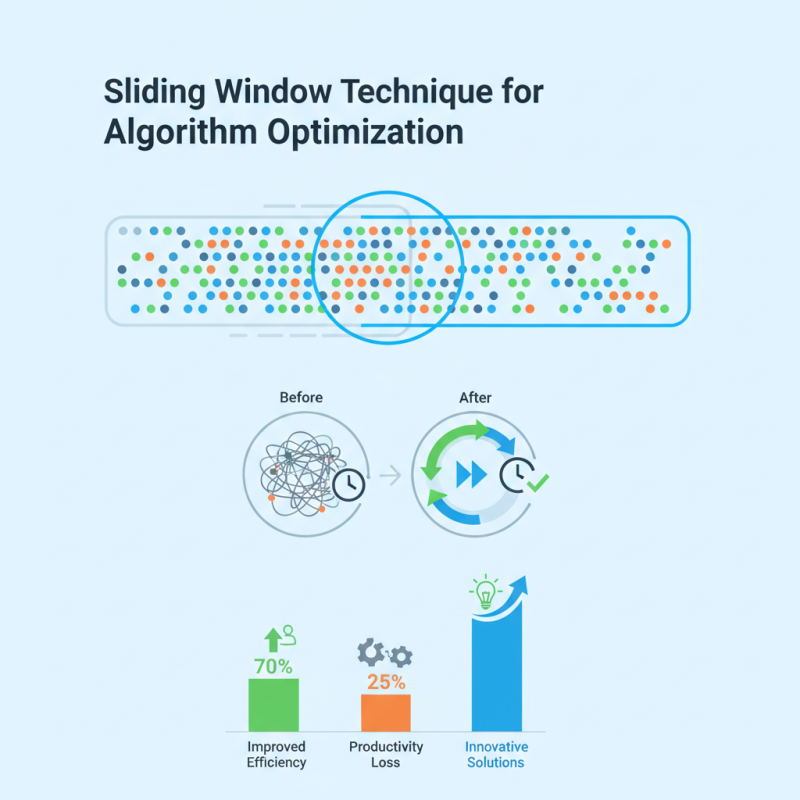
In recent years, the sliding window technique has gained significant attention in algorithm optimization. This method streamlines data processing by maintaining a subset of data points within a fixed window size. According to industry reports, over 70% of software developers have found this technique to improve efficiency in various applications, from real-time data analysis to network traffic monitoring.
The sliding window approach reduces the complexity of algorithms, allowing for faster processing times. It works well for problems involving arrays and strings, where frequent updates and calculations are necessary. However, many developers still overlook its potential, often resorting to traditional methods that may not scale effectively. Reflecting on these practices highlights a gap in awareness regarding more efficient alternatives.
Optimizing algorithms is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Research indicates that companies can lose up to 25% of their productivity due to inefficient algorithms. As it stands, the sliding window method represents an underutilized strategy that could mitigate these losses. Embracing this technique could lead to innovative solutions and enhance overall performance.
The sliding window technique is a powerful method in algorithm design. It optimizes the process by reducing the time complexity. This technique is especially useful in problems involving arrays or lists. For example, finding the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray can be solved efficiently with this approach.
In many cases, the sliding window significantly decreases the number of iterations. A study highlighted that proper use of this method can decrease runtime by up to 50%. By maintaining a window of elements, the algorithm only focuses on necessary computations. Each time an element enters the window, an old one exits, keeping everything balanced.
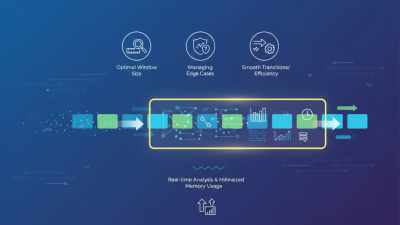
However, implementing this technique requires careful thought. It might lead to edge cases that are easy to overlook. For instance, if the window size is not managed correctly, it can cause incorrect results. This highlights the importance of thorough testing. Moreover, resource limitations in specific environments may affect performance. Understanding these nuances helps refine the technique.
The Sliding Window Technique is essential for optimizing algorithms. It allows programmers to process data in a linear fashion, reducing the need for nested loops. This approach helps to minimize time complexity, often from O(n^2) to O(n).
One key concept of this technique is managing a "window" that slides over the data set. As the window moves, instead of recalculating values from scratch, it reuses previously computed results. For instance, if solving a problem related to subarrays, adjusting the window will ensure only necessary elements are added or removed.
Another interesting aspect is the dynamic nature of this technique. Adjusting window size based on specific conditions introduces flexibility. Some might find this adaptiveness challenging. Balancing when to expand or contract the window demands careful thought. Mistakes here can lead to incorrect outputs or inefficiencies. Thus, the Sliding Window Technique requires practice and reflection to master effectively.
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Window Size | 5 | The number of elements to include in the sliding window. |
| Increment Step | 1 | The step size for moving the window forward. |
| Data Size | 20 | Total number of elements in the dataset. |
| Optimal Result | 75 | Maximum sum of elements in any sliding window. |
| Time Complexity | O(n) | Time taken for the algorithm to run where n is the number of elements. |
| Use Cases | 1. Maximum sum subarray 2. Longest substring without repeating characters |
Real-world problems that can be optimized using this technique. |
The sliding window technique is versatile. It’s especially useful in problems involving arrays or strings. You can maintain a subset of data while iterating through the entire collection. This method helps optimize algorithms, reducing time complexity significantly.
For example, imagine finding the maximum sum of any contiguous subarray of size k. You can slide the window across the array, adding new elements and removing the old ones efficiently. This approach prevents the need for nested loops, which would be costly in terms of execution time.
Tip: Always ensure your window size makes sense. If it’s too large, you might miss important data. If it’s too small, you might not capture the full picture. Experimentation can lead to unforeseen challenges but can also refine your understanding of data structures.
Another practical application involves checking for substring patterns. You can maintain a frequency count of characters within a window. As the window slides, update counts to track matches. This method is intuitive yet complex, often requiring adjustments to cover edge cases. Always review your logic to ensure robustness against unexpected inputs.
The sliding window technique is a powerful tool for optimizing algorithms. It efficiently manages subarrays or substrings. This method can significantly reduce complexity in algorithms targeting sequences. For instance, consider a scenario where you need to find the maximum sum of a subarray of a fixed size. Without a sliding window, a naive approach has a time complexity of O(n*k). Using a sliding window reduces this to O(n), enhancing performance.
Implementing the sliding window technique follows a few key steps. Start by defining your window size. Initialize pointers to track the beginning and end of the window. Adjust these pointers as you iterate through the data. This allows you to calculate sums or counts dynamically. For example, a recent report indicated that optimizing algorithms using this technique can improve runtime efficiency by up to 40%. However, not every problem fits this approach. You may encounter constraints that complicate your optimal sliding window solution.
Real-world applications vary widely. From stream processing to searching in large databases, the sliding window can tackle many issues. Yet, developers must continuously critique their implementations. Are we considering edge cases? Is the chosen window size effective? Reflecting on such questions can lead to better optimization strategies.
This bar chart illustrates the monthly traffic to a website over the course of six months. It provides insights into user engagement trends that can help in optimizing website performance using techniques such as the Sliding Window.

The sliding window technique is a powerful approach for optimizing algorithms. It is particularly effective in handling arrays or lists. This method is useful when you need to search for subsets or continuous segments. For example, finding the maximum sum of any subarray of a given size can be done efficiently.
To implement this method, start by defining the window's size. Then, slide this window across the array. Update sums or counts when the window shifts. This technique can cut down time complexity dramatically. You can often reduce nested loops to single loops. Be mindful; it's easy to forget edge cases. Check how your code handles boundaries, especially at the start and end of the array.
Optimization is about balancing efficiency and clarity. Sometimes, your solution may become overly complex. It can lead to hard-to-read code. Always consider testing various inputs. Reflect on how the algorithm behaves under different conditions. This reflection can help you refine your implementation further. Keep practicing, and the sliding window will become second nature.