Locally made
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, efficient data management techniques are essential for optimizing application performance. One such powerful technique is the "sliding window" method, which allows developers to process and analyze data in a more structured and efficient manner. This technique is particularly beneficial when dealing with streaming data or large datasets where it is impractical to examine the entire set at once. By maintaining a fixed-size subset of data, the sliding window approach enables real-time analysis and minimizes memory usage, making it an invaluable tool in various programming scenarios.
Implementing the sliding window technique effectively can substantially enhance the speed and efficiency of your projects. However, it requires a solid understanding of its fundamental principles and practical considerations. In this article, we will explore essential tips for successfully incorporating the sliding window technique into your workflows. From establishing the optimal window size to managing edge cases and ensuring smooth transitions, these insights will help you leverage the full potential of this technique. Whether you are tackling algorithm challenges or optimizing data processing tasks, mastering the sliding window approach can lead to significant improvements in your project's overall performance.

The sliding window technique is a powerful approach used in various fields such as computer science, signal processing, and even data analysis. Fundamentally, it involves creating a "window" that moves across a data set, allowing for the exploration of subsets while maintaining a focus on efficiency. By adjusting the window size and position, this technique enables the efficient processing of data streams without the need to re-evaluate entire sets repeatedly. This is particularly effective in problems related to arrays and strings, such as finding subarrays that meet specific criteria or calculating maximum values in a continuously changing dataset.
Applications of the sliding window technique can be seen in diverse scenarios, from optimizing algorithms in competitive programming to real-time data monitoring in software development. For instance, when implementing a search algorithm in a large dataset, utilizing a sliding window can significantly reduce the time complexity by limiting the scope of examination to a defined segment. Similarly, in network monitoring, the sliding window allows for the efficient tracking of data packets, facilitating real-time analysis while minimizing processing delays. Overall, the sliding window technique enhances performance and provides a structured method for handling data challenges effectively.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Application | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Understand the Problem Requirement | Data processing | Finding maximum sum in a subarray |
| 2 | Define the Window Size | Problem modeling | Length of fixed number of elements |
| 3 | Use Two Pointers Approach | Array traversal | Sliding window minimum/maximum |
| 4 | Update the Window Efficiently | Performance optimization | Dynamic sum calculations |
| 5 | Consider Edge Cases | Robustness | Empty arrays or few elements |
The sliding window technique is a powerful method used in various domains, particularly in computer science and data analysis. This technique is particularly beneficial in scenarios where large datasets need to be processed efficiently. For instance, in time-series analysis, the sliding window method allows practitioners to analyze subsets of data within a defined time frame, thereby enabling the detection of trends and patterns that may not be immediately visible in the complete dataset. According to a report by the International Data Corporation (IDC), the volume of data generated worldwide is expected to reach 175 zettabytes by 2025, making effective processing methods like sliding windows crucial for timely decision-making.
Another suitable application for the sliding window technique can be found in network traffic analysis, where real-time monitoring and anomaly detection are paramount. A study by Gartner highlighted that businesses are increasingly focusing on real-time analytics, with 70% of organizations stating that real-time insights significantly enhance their operational efficiency. By implementing a sliding window approach, IT specialists can examine packets of information as they flow in and out, quickly identifying unusual activity that may indicate potential threats or performance bottlenecks. This responsive strategy not only facilitates better resource management but also ensures more robust network security.
In summary, the sliding window technique proves invaluable across various scenarios, from data analysis to network monitoring, helping organizations harness the growing volume of data effectively. Its adaptability and efficiency align well with the industry's demand for real-time insights and enhanced operational capabilities.
The sliding window technique is essential for optimizing algorithms that require frequent array or string manipulation. This method allows developers to efficiently track subarrays or substrings without needing to repeatedly recalculate stats for every potential segment. According to a report by the Computer Science Research Institute, algorithms employing sliding window strategies have shown up to a 40% reduction in computational complexity compared to brute-force approaches.
To design a sliding window algorithm, start by defining the size of the window based on the problem requirements. For example, with fixed-size windows, you will maintain a count of the elements and gradually slide the window over your dataset. It’s crucial to ensure that you adjust the count accurately as the window expands or contracts, which can directly affect the program's performance. Maintain clarity in your code and frequently check boundary conditions to prevent unexpected errors.
Tips for successful implementation include starting with a well-defined goal for what the window will capture, ensuring that your pointers or indices are managed correctly, and utilizing data structures that support rapid access, such as hash tables. According to a survey by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), over 60% of developers reported that adopting the sliding window technique led to a significant increase in their project’s efficiency, making it a widely recommended approach in algorithm design.
Implementing the sliding window technique can transform how projects manage data streams, but it comes with its set of challenges. One common issue is how to effectively manage the window's size and position, especially in real-time applications. Developers often struggle with determining the optimal size for their sliding windows, which can lead to performance bottlenecks or excessive data retention. To address this, it is crucial to analyze the specific use case and the nature of the data being processed. Start by experimenting with different window sizes and carefully monitor system performance and response times to find the balance that works best for your project.
Another challenge is handling overlapping windows. When data points fall into multiple windows, the risk of redundant processing can increase significantly. To mitigate this, consider implementing a tiered sliding window approach, where one window feeds into another, allowing for more efficient data processing without losing crucial information. Additionally, ensure that your data structures can handle concurrent modifications, especially in multi-threaded environments, to maintain accuracy and efficiency during data retrieval.
Lastly, integration with existing systems can pose difficulties, particularly when dealing with legacy systems that may not be designed for such dynamic data handling. To overcome this, a gradual integration plan that introduces the sliding window concept in phases can be beneficial. This allows for adjustments based on feedback and performance metrics at each stage, ensuring that the implementation is both robust and seamless. As you navigate these challenges, always keep in mind the importance of thorough testing and validation to guarantee that the sliding window implementation meets your project's requirements.
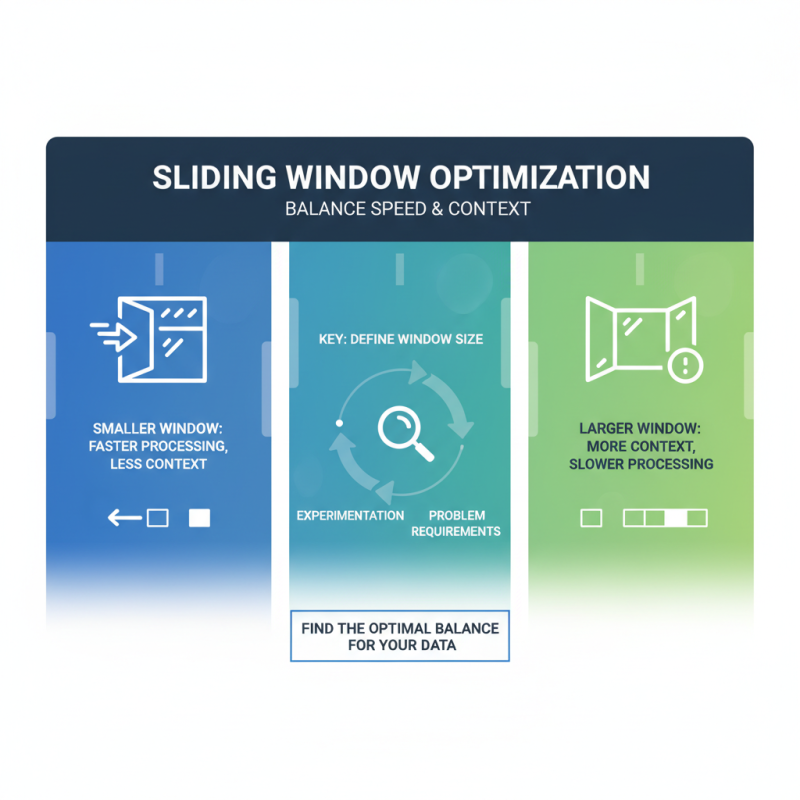
When implementing the sliding window technique in your projects, optimizing performance is crucial to ensure efficiency and ease of use. One fundamental practice is to carefully define the size of the window based on the specific requirements of the problem at hand. A larger window size can capture more context but may lead to increased processing time and memory usage. Conversely, a smaller window can enhance speed but might miss critical data. Therefore, experimenting with different window sizes during the initial phases can help identify the optimal balance for your specific application.
Another best practice involves employing a systematic approach to data handling within the sliding window. Buffer management is essential; ensure that data is appropriately added and removed from the current window to prevent memory overflow and maintain optimal performance. Additionally, implementing efficient algorithms for data aggregation within the window can significantly reduce processing time. Techniques such as maintaining a deque for dynamic data retrieval or using hash maps for quick access can enhance the effectiveness of the sliding window implementation. By focusing on these strategies, you can achieve a significant boost in performance and reliability in your projects.